[ad_1]
- The price of gold increases as tThe US dollar weakens due to upbeat data from China, which improves risk appetite.
- US yields hold firm on lower Fed rate cut expectations for June.
- This week, the Federal Reserve’s decision and guidance on interest rates will be closely watched.
The price of gold (XAU/USD) rises in the early hours of the New York session on Monday as the US dollar faces pressure. The US Dollar Index (DXY) is trading slightly lower at 103.40 on higher risk appetite. The attractiveness of risk-sensitive assets strengthened due to the strong recovery in China’s retail sales and industrial production data for February, indicating an improvement in China’s domestic demand.
Lower expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will cut interest rates at the June policy meeting have strengthened yields on interest-bearing assets. US 10-year Treasury yields have extended their rise to 4.33%, up 0.45%. Higher US bond yields tend to increase the opportunity cost of holding an investment in unprofitable assets like gold.
This week, the price of gold will be guided by the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decision, which will be announced on Wednesday. The Federal Reserve is widely expected to keep interest rates unchanged in the 5.25%-5.50% range. Therefore, the main focus will be on interest rate guidance, which will be provided through the publication of the so-called dot plot, a quarterly updated chart showing Federal Reserve officials’ interest rate projections for various periods of time.
Daily Market Factors Summary: Gold Price Rises as US Dollar Falls, US Yields Extend Higher
- Gold price rises back above $2,160 as the US dollar comes under pressure. Investors await key interest rate meetings from several central banks this week. The price of gold in the short term will be guided by the monetary policy decision of the Federal Reserve.
- The CME FedWatch tool shows that a firm decision is certain for the March meeting. Market participants will especially focus on the dot plot, which indicates all authorities’ expectations for interest rates over time and the latest economic projections. Investors will be looking for signs on when the Federal Reserve might start cutting interest rates.
- The December dot plot showed that authorities see no need to raise interest rates further and are forecasting three rate cuts this year. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and associated inflation indicators for the first two months of 2024 have not supported three rate cuts as Fed policymakers want price pressures to ease for months to gain confidence when inflation will return to the 2% target. This could lead to fewer rate cut projections from Fed policymakers.
- Meanwhile, market expectations are leaning toward the June policy meeting, when the Federal Reserve will begin cutting key interest rates. However, the chances of a rate cut in June have been significantly reduced, as the consumer and producer price indices were surprisingly stubborn in February. The CME FedWatch tool shows the probability of a rate cut at 57%, up from 72% before the inflation data was released.
- Later this week, investors will focus on the S&P preliminary global manufacturing PMI for March. The manufacturing PMI is expected to fall to 51.7 from 52.2 in February.
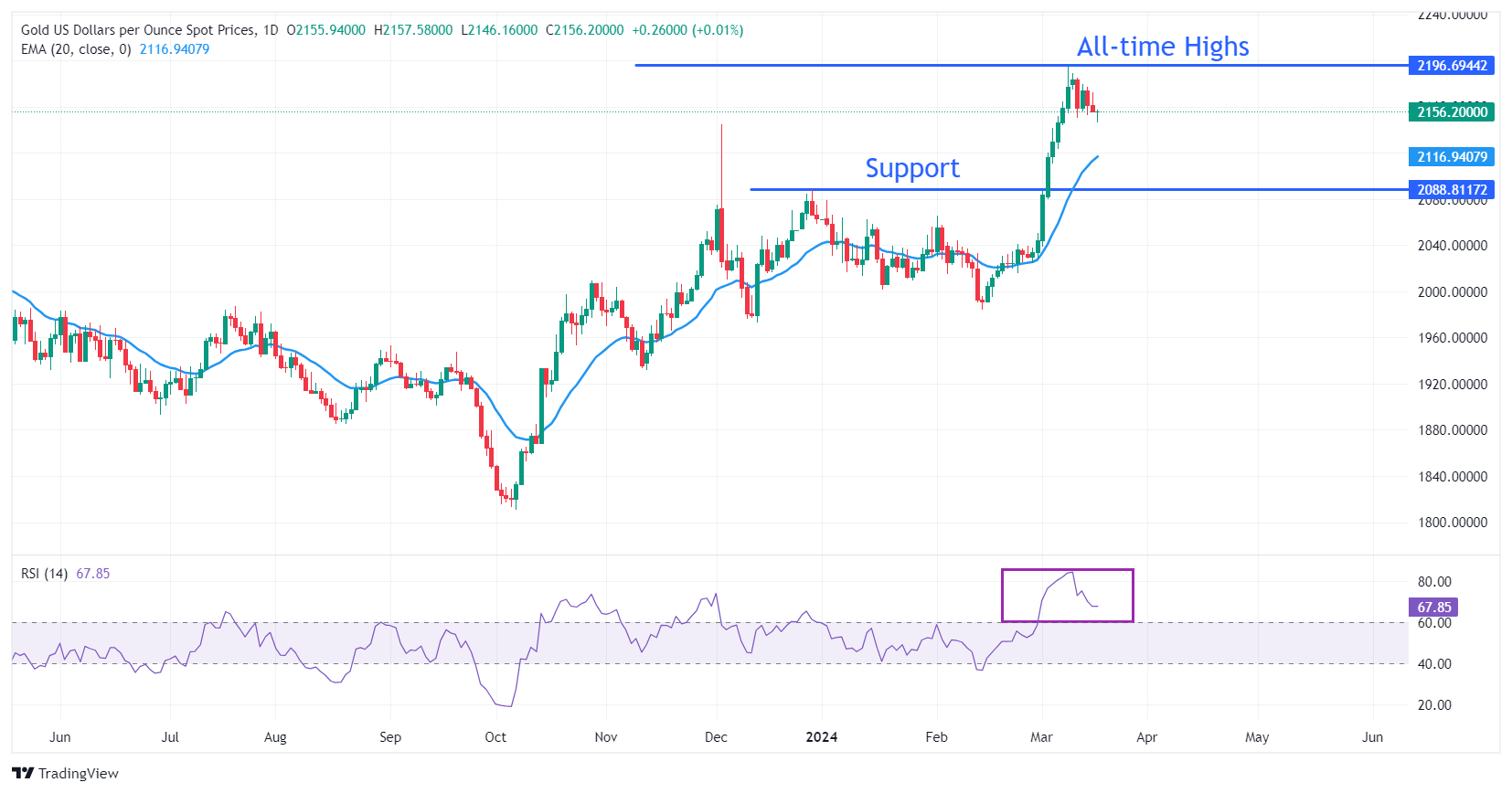
Technical Analysis: Gold Price Aims to Stay Above $2,160
Gold price recovers sharply after hitting a new weekly low around $2,145. As the divergence between the two decreases, the precious metal could continue its decline towards the 20-day EMA at $2,097. After a wide divergence, the asset tends to face a mean reversion movement, resulting in a price or time correction.
On the downside, the December 4 high near $2,145 and the December 28 high at $2,088 will act as important support levels.
The 14-unit Relative Strength Index (RSI) retreats from its high near 84.50, although bullish momentum remains active.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Federal Reserve
Monetary policy in the United States is determined by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Federal Reserve has two mandates: to achieve price stability and to promote full employment. Your main tool to achieve these goals is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation is above the Federal Reserve’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, raising borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US dollar (USD) as it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the dollar.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, at which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Federal Reserve officials: the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the eleven remaining regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms. on a rotating basis. .
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Federal Reserve substantially increases the flow of credit in a stagnant financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Federal Reserve’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Federal Reserve printing more dollars and using them to buy high-quality bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops purchasing bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal of maturing bonds it owns to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US dollar.