[ad_1]
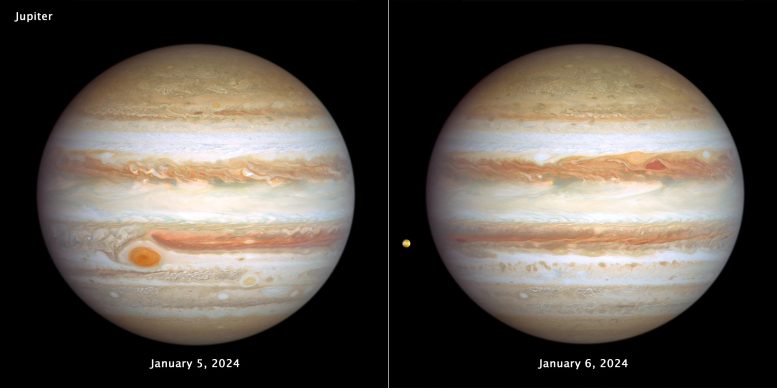
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured new images of Jupiter on January 5-6, 2024, revealing dynamic weather patterns and notable storms such as the Great Red Spot and Red Spot Jr. The observations are part of the annual Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy program , which also highlighted Io’s volcanic activity and surface features. Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC)
Cyclones, wind shear and violent storms churn through Jupiter’s atmosphere
The largest and closest of the outer giant planets, JupiterThe colorful clouds present a kaleidoscope of ever-changing shapes and colors. This is a planet where there is always stormy weather: cyclones, anticyclones, wind shear and the largest storm in the solar system, the Great Red Spot.
Jupiter has no solid surface and is perpetually covered with clouds of largely ammonia ice crystals that are only about 30 kilometers thick in an atmosphere that is tens of thousands of kilometers deep and give the planet its banded appearance. .
The bands are produced by air flowing in different directions at different latitudes with speeds approaching 350 miles per hour. The lighter-toned areas where the atmosphere rises are called zones. The darker regions where the air falls are called belts. When these opposing flows interact, storms and turbulence appear.
Hubble tracks these dynamic changes every year with unprecedented clarity, and there are always new surprises. The numerous large storms and small white clouds seen in the latest Hubble images are evidence of a lot of activity in Jupiter’s atmosphere right now.
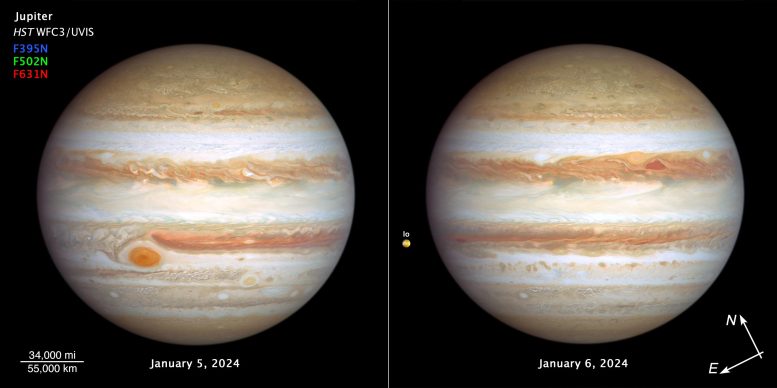
Jupiter has stripes of brownish orange, light gray, soft yellow and cream tones. Many large storms and small white clouds dot the planet. The largest storm, the Great Red Spot, is the most prominent feature in the lower left third of this view. At the bottom right is a smaller reddish anticyclone, Red Spot Jr. Another small red anticyclone appears near the top center of the image. In the upper right center of the right image, a pair of storms appear side by side: a deep red triangle-shaped cyclone and a reddish anticyclone. Toward the far left of the image is Io, Jupiter’s small moon. The variegated orange color is where the volcanic deposits are seen on the surface of Io. Credit: NASA, ESA, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC)
Hubble Space Telescope Tracks Jupiter’s Stormy Weather
The giant planet Jupiter, in all its splendor, is visited again by POT‘s Hubble space telescope in these latest images, taken from January 5 to 6, 2024, which capture both sides of the planet. Hubble monitors Jupiter and the other outer planets of the solar system each year under the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy Program (OPAL). This is because these great worlds are shrouded in clouds and mists churned by violent winds, creating a kaleidoscope of ever-changing weather patterns.
(left image) – Large enough to swallow the Earth, the classic Great Red Spot features prominently in Jupiter’s atmosphere. At the bottom right, at a more southern latitude, is a feature sometimes called Red Spot Jr. This anticyclone was the result of merging storms in 1998 and 2000, and first appeared red in 2006 before returning to a pale beige color in subsequent years. This year it is a little redder again. The origin of the red coloration is unknown, but it may be due to a variety of chemical compounds: sulfur, phosphorus, or organic material. Staying in its lanes, but moving in opposite directions, Red Spot Jr. passes the Great Red Spot about every two years. Another small red anticyclone appears in the far north.
(right image) – Storm activity also appears in the opposite hemisphere. A pair of storms, a deep red cyclone and a reddish anticyclone, appear side by side to the right of center. They look so red that, at first glance, it looks as if Jupiter has skinned its knee. These storms spin in opposite directions, indicating an alternating pattern of high and low pressure systems. In the case of the cyclone, an upwelling occurs at the edges with clouds descending in the center, causing a clearing of the atmospheric haze.
Credit: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Lead Producer: Paul Morris
The storms are expected to bounce off each other because their opposite clockwise and counterclockwise rotation causes them to repel each other. “The many large storms and small white clouds are a hallmark of a lot of activity happening in Jupiter’s atmosphere right now,” said OPAL project leader Amy Simon of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt. , Maryland.
Toward the left edge of the image is the innermost Galilean moon, Io, the most volcanically active body in the solar system, despite its small size (only slightly larger than Earth’s moon). Hubble resolves volcanic deposits on the surface. Hubble’s sensitivity to blue and violet wavelengths clearly reveals interesting surface features. In 1979 NASA traveler 1 The spacecraft discovered Io’s pizza-like appearance and volcanism, to the surprise of planetary scientists because it is a very small moon. Hubble picked up where Voyager left off, monitoring restless Io year after year.
The Hubble Space Telescope images used in this animated scientific visualization feature a complete rotation of the giant planet Jupiter. This is not a real-time movie. Instead, Hubble snapshots of the colorful planet, taken January 5-6, 2024, have been photomapped onto a sphere and then the model is rotated in animation. The planet’s actual rotation speed is almost 10 hours, which can be easily plotted by watching the Great Red Spot come and go with each complete rotation. Hubble monitors Jupiter and the other planets in the outer solar system each year under the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program. Credit: NASA, ESA, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC), Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
The Hubble Space Telescope has been operating for more than three decades and continues to make groundbreaking discoveries that shape our fundamental understanding of the universe. Hubble is an international cooperation project between NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. Goddard also conducts mission operations with Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble and Webb science operations for NASA. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, in Washington, DC

This series of 12 panels of Hubble Space Telescope images, taken January 5-6, 2024, features snapshots of one complete rotation of the giant planet Jupiter. The Great Red Spot can be used to measure the planet’s actual rotation rate of almost 10 hours. The innermost Galilean satellite, Io, is seen in several frames, along with its shadow crossing Jupiter’s cloud tops. Hubble monitors Jupiter and the other planets in the outer solar system each year under the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program. Credit: Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC)

